Overview
 The Carolina Data Warehouse for Health (CDW-H) houses clinical health records for all UNC Hospitals patients. These records are a valuable source of data for researchers. In addition to enabling access for legitimate healthcare and research purposes, the
The Carolina Data Warehouse for Health (CDW-H) houses clinical health records for all UNC Hospitals patients. These records are a valuable source of data for researchers. In addition to enabling access for legitimate healthcare and research purposes, the
CDW-H must protect against loss of these records to ensure patient privacy and security.
RENCI’s Role
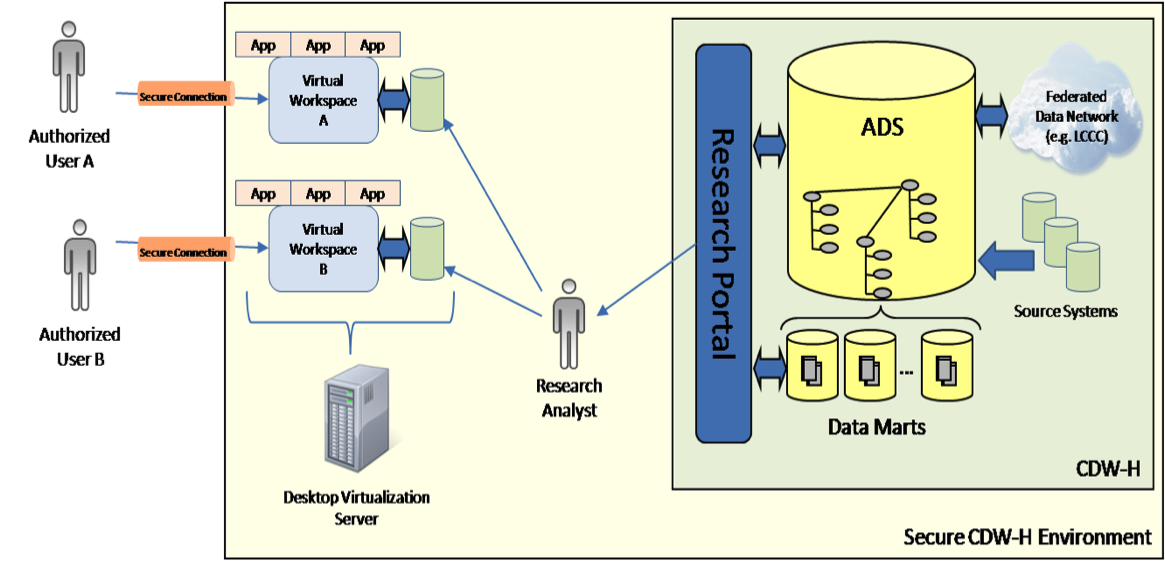
RENCI, in collaboration with The North Carolina Translational and Clinical Sciences (NC TraCS) Institute, the UNC School of Information and Library Science (SILS), UNC Hospitals, and UNC ITS Research Computing, developed what was first called the Secure Medical Workspace (SMW) system to enable the CDW-H to provide researchers and healthcare professionals secure access to patient records. In its second phase, the project has been broadened and renamed the Secure Research Space (SRS).
Phase I, known as SMW, was designed as a combination of secure centralized infrastructure with virtualization and data leakage protection technologies to allow researchers to manipulate and analyze research data while ensuring that sensitive patient information remains within the SMW environment. Authorized researchers use SMW from their local computing devices over a secure network connection to a dedicated virtual workspace containing data provisioned to them. The system provides researchers access to standard analytical software packages for working with their data as well as storage space for saving output files securely. The SMW system is now available for use UNC-wide.
Phase 2, or SRS, was developed by RENCI in collaboration with the UNC Health Care System and Fabian Monrose, PhD, a faculty member at UNC- Chapel Hill, Computer Science department. SRS is a novel, comprehensive solution to the challenge of using sensitive patient data for research purposes. The SRS provides approved researchers with easy access to sensitive patient data for approved clinical research in a secure virtual workspace. It prevents researchers from removing that data from a central, secure, storage environment.
Key aspects of the SRS include:
- Two-factor identification authentication to gain access to the secure space.
- Virtualization technology to provide access to sensitive data and analysis applications within the secure environment and without the ability to remove any sensitive data.
- Preconfigured virtual machine images that conform to and automatically implement UNC’s security policies.
- Use of encryption for data in motion and data at rest and IT management capabilities to provide for easy administration of the entire solution and equip IT administrators with an audit trail of data removed from the secured environment.
The SRS architecture incorporates commercial technologies that were assessed against a comprehensive matrix of features required by UNC’s institutional security policies.
Deployments
UNC adopted the SRS as a central offering of its security plan following a comprehensive assessment of the technology and the system is deployed for data management in three large, data-intensive research projects: NCGENES (North Carolina Clinical Genomic Evaluation by NextGen Exome Sequencing) in the department of genetics; SAS Healthcare Analytics and the UNC’s Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center and SAS; and the Integrated Cancer Information and Surveillance System at the Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Project Team
- Michael Shoffner (Project Leader)
- Fan Jiang
- Phil Owen
- Charles Schmitt
- Erik Scott
- Jan Werner
Partners
Funding
Clinical and Translational Science Awards, National Institutes of Health



